UGT-Assisted Glycosylation in Drug Discovery: Unlocking Potential with GlycoDepot’s 386 Enzyme Library
Introduction
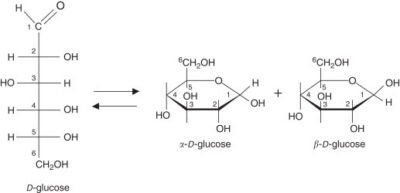
Enzyme-based glycosylation, in which a sugar chain is conjugated to a small molecular compound, is becoming a transformative technology in present-day drug discovery. It is a biochemical transformation that may enhance the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characteristics of a drug candidate, including solubility, stability during metabolism, half-life, and interaction with the target. Furthermore, glycosylation may improve the compound’s cytotoxicity and increase its penetration into biological membranes, which is especially useful in drug design and the development of safe, more efficient therapeutics.
The most closely related group in this strategy would be UDP-glycosyltransferases (UGTs), a heterogeneous group of enzymes that transfer glycosyl groups (e.g., glucose, glucuronic acid, rhamnose) attached to activated sugar donors (e.g., UDP-glucose), to a variety of acceptors, notably natural products, drugs, and xenobiotics. Such enzymatic reactions improve the diversity of glycosylated derivatives but also allow fine-tuning of compound activity.GlycoDepot produces 386 UGT enzymes in extensive quantities with an extensive range of sources and engineering labor, including microbial, plant, and mammalian. Such a library provides a disturbing substrate and screening platform, enabling researchers to rapidly identify the optimal enzyme-substrate combinations in high-throughput and pathway optimization. We want to streamline and accelerate the discovery and preclinical development process by finding the full potential of glycosylation-based molecular design.
Fig.1. Reaction mechanism of UGT
Source: Image sourced from Researchgate.
What are UDP Glycosyltransferases?
UDP-glycosyltransferase (UGT) enzymes are a group of enzymes in charge of glycosylating small molecule acceptors with the transfer of the sugar residues, typically of the activated donor groups such as UDP-glucose. This is a biochemical reaction referred to as glycosylation, and it has become essential in altering the physicochemical characteristics of compounds that are closely related to the conduct of pharmacology. Unlike in nature (as a common mechanism of detoxification), glycosylation can be used in drug discovery as a molecular tuning event to increase the therapeutic utility of lead compounds. Through the binding of specific sugar moieties, UGTs are capable of affecting solubility, metabolic stability, toxicity, and even targeting efficiency.
Key Benefit in Drug Discovery:
- Heightened Solubility:
The sugar residues improve the hydrophilicity of those drugs that are not poorly soluble in water and increase their bioavailability.
- Enhanced stability:
The glycosylated compounds tend to be less susceptible to enzyme or chemical breakdown, increasing their half-life.
- Lower toxicity:
Through the process of glycosylation, functional groups that are reactive or toxic can be masked, thereby enhancing safety profiles but not efficacy.
- Potential Prodrug:
Glycosides may serve as prodrugs, where the active molecule becomes available in particular tissues in an enzymatic reaction, i.e., targeted and conditional activation of the drug.
All these benefits mean that UGT-mediated glycosylation can be an effective solution to optimizing the pharmacokinetics and pharmacological activities of emerging drug candidates.
Fig. 1. General UGT reaction scheme represented by UGT71G1
Source: Image sourced from mdpi.com
Key Innovations in UGT-Driven Drug Development
- Enzyme Promiscuity:
The substrate specificity exhibited by UGTs is wide. They are sometimes strikingly selective and proceed to convert only a few specific types of aglycon into a certain few types of product, or they are extremely fast and will transform a broad range of different kinds of molecular support groups into an equally broad range of different kinds of product groups. Enzymatic flexibility is both a blessing and a curse; it presents possibilities for identifying novel glycosylated pharmaceutical candidates and also causes a headache to the process of ensuring product consistency and regio- and stereoselectivity in a glycosylation reaction.
- High-Throughput Screening:
It is now also feasible, through the use of fluorescent-based UDP detection tests and other label-free analytical tools, to screen hundreds of UGTs at once in terms of activity against target molecules. The high throughput nature of these platforms practically speeds up the enzyme-to-substrate compatibility analysis versus the conventional chromatography-based approaches, leading to lead optimization and development cycles being minimized.
- Protein Engineering and Synthetic Biology:
Recent years have seen a breakthrough in enzyme engineering and directed evolution whereby the UGTs can now be fine-engineered to maximize their performance. It is now possible to engineer UGT variants with:
- Greater catalytic performance.
- Enhanced sugar donor selectivity (e.g., UDP-glucose, UDP-galactose).
- Increased industrial stability in operation.
Furthermore, synthetic biology methods have been applied to the expression of UGTs in microbial hosts with a view towards the use of such microorganisms to produce glycosylated molecules at scale and cost-effectively to permit preclinical or commercial development of these compounds.
Applications in Action
UGT-Assisted Glycosylation enzymes are very versatile, far beyond the scope of pharmaceuticals. As a technology that enables modification of molecular structures in the field of glycosylation, its potential is now being exploited in many areas beyond food safety, including the development of functional ingredients reflecting practical application and creating innovation.
- Mycotoxins detoxification:
Probably one of the most influential uses of UGTs is their implementation in food detoxification. A thorough screening program defined certain plant-origin UGTs in a position to glycosylate deoxynivalenol (DON), a harmful mycotoxin generated by strains of Fusarium. The generated DON-glucosides were much less toxic, which demonstrates glycosylation as a potent approach towards enhancing food safety and protection of crops. The strategy is particularly exciting in the development of safer food products based on grain and animal feed.
- Biosynthesis of Natural Sweeteners:
In the food industry and nutraceutical industry, UGT has also been engineered to increase the biosynthesis of mogroside derivatives, a highly sweet compound of monk fruit origin. The sweeteners with better glycosylation patterns were found to be sweeter and stable, and the working model opened doors to designing natural calorie-free sweeteners. This application is an example of the methods that UGTs can use to make health-focused food additives in a sustainable and biocatalytic way.
The GlycoDepot Advantage
GlycoDepot is a strong Glycosylation Innovation empowering tool that strengthens researchers and developers. We have created a proprietary library of 386 UGT enzymes, all recombinantly produced in E. coli to be as accessible, scalable, and high-performance as possible to academic and industrial use. GlycoDepot gives you the tools to speed up your search, whether you are monitoring newly discovered glycosylation signatures or maximizing biocatalysts across the production tiers.
GlycoDepot Platform characteristics:
- Diversity:
The substrate specificity of our enzyme library is wide, covering a broad array of UGT families. It allows you to glycosylate structurally diverse small molecules – flavonoids and alkaloids, as well as drug-like scaffolds, meaning you have more flexibility in your compound development.
- High-Production Expression:
Each of the UGTs is expressed recombinantly in E. coli, guaranteeing highly predictable and high-yield enzyme product formation. This enables confident use in screening, scale-up, and downstream.
- Screening Support:
We supply fluorescent UDP-detection assay kits so you can rapidly determine enzyme activity on a range of different substrates using high-throughput formats.
- Customization:
Want a UGT-Assisted Glycosylation customized to your compound or pathway? Our group provides enzyme engineering, such as active-site optimization, donor specificity fine-tuning, etc., on a service-for-service basis.
- Specific Data Sheets:
Each enzyme in our catalog is supported by a detailed biochemical characterization, such as substrate preferences, ideal reaction parameters, and kinetic constants–enabling you to make informed reagent decisions much quicker.
Streamlined Workflow for Drug Discovery
We are texting a workflow at GlycoDepot that streamlines glycosylation technology straight into the drug development pipeline of the researcher-makers, researchers on a step-wise basis, fast, efficient, and economical.
- Submit Your Little Molecule Substrates:
Send your lead compounds or small molecule libraries to us to kick off. Our platform can process natural items, synthetic medications, or experimental structures.
- Screen with the 386-UGT Panel:
Our vast UGT enzyme library enables high-throughput screening with the aid of fluorescent UDP-detection assays to provide accuracy during the discovery of enzyme-substrate matching.
- Obtain an Illustrated Activities Profile:
Among the findings that will help evaluate the most promising routes of enzymatic procedures, you will receive a detailed report including conversion rates, glycosylation positions, and enzyme specificity data.
- Enzyme selection and optimization:
Select the highest quality UGTs, and when that is insufficient, simply utilize our workforce to create bespoke enzymes- activity, stability, or even donor specificity made to your exact requirements.
- Development and Scale-Up:
When optimized, UGTs of interest can be incorporated into a microbial host or a bioprocess to scale up to a pilot, which will lead to preclinical development and more.
This fully-integrated process significantly increases speed, degree of uncertainty, and cost-effectiveness that normally comes with glycosylation-based drug development-making you one step closer to breakthrough therapeutics, much sooner.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Though UGT-assisted glycosylation is at its promising stage, it is still:
- Control Problems: Control of regio- and stereoselectivity is difficult.
- Scalability: Needs cost-effective and efficient processes of production.
- Wider substrate compatibility: Larger-scale growth is required.
- Enzyme Integration: A Perfect choice to have multi-step biosynthesis in engineered cells.
With the help of high-tech screening assays and a very impressive enzyme inventory, GlycoDepot is leading the charge in breaking these blocks.
Conclusion:
UGT-assisted Glycosylation is helping to define drug discovery in the future, enabling selective and efficient glycosylation. The 386-enzyme library of GlycoDepot will allow researchers to enhance the therapeutic capabilities of small molecules, rendering the drugs more efficient, stable, and patient-friendly.
The future is glycosylation. GlycoDepot makes it reachable.
References:
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/5/2782
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Reaction-mechanism-of-UGT-Reaction-
Della Gala, Valeria, et al. “Plant-derived UDP-glycosyltransferases for glycosylation-mediated detoxification of deoxynivalenol: Enzyme discovery, characterization, and in vivo resistance assessment.” Toxins 17.4 (2025): 153.
| Della Gala, Valeria, et al. “Plant-derived UDP-glycosyltransferases for glycosylation-mediated detoxification of deoxynivalenol: Enzyme discovery, characterization, and in vivo resistance assessment.” Toxins 17.4 (2025): 153. |
Zhao, Z., Chen, J., & Yuwen, W. (2025). Applications and Challenges of Pullulan in China’s Food Industry. ACS Agricultural Science & Technology.
Model, TWST Stock Price Forecasting. “Twist Bio’s (TWST) Analysts Predict Growth, Citing Strong Demand.” Outlook 1: B3.